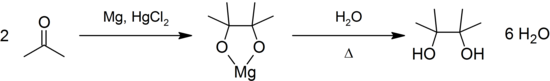Pinacol
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dimethylbutane-2,3-diol
|
|
| Other names
2,3-Dimethyl-2,3-butanediol
Tetramethylethylene glycol 1,1,2,2-Tetramethylethylene glycol Pinacone |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.849 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 118.174 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 0.967 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 40 to 43 °C (104 to 109 °F; 313 to 316 K) |
| Boiling point | 171 to 173 °C (340 to 343 °F; 444 to 446 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S24 S25 |
| Flash point | 77 °C (171 °F; 350 K) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Pinacolone |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Pinacol is a white solid organic compound. It is a diol that has hydroxyl groups (-OH) on vicinal carbon atoms.
It may be produced by the pinacol coupling reaction from acetone:
As a vicinal-diol, it can rearrange to pinacolone by the pinacol rearrangement, e.g. by heating with sulfuric acid:
Pinacol can be used with borane and boron trichloride to produce useful synthetic intermediates such as pinacolborane, bis(pinacolato)diboron, and pinacolchloroborane.
...
Wikipedia