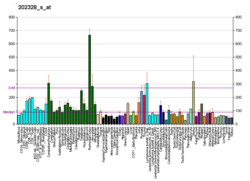
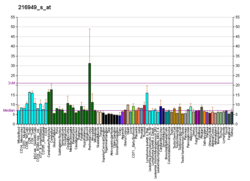
PKD1
Polycystin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PKD1 gene.
Splice variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for PKD1. The gene is closely linked to six pseudogenes in a known duplicated region on chromosome 16p.
Polycystin-1 is a glycoprotein which contains a large N-terminal extracellular region, multiple transmembrane domains and a cytoplasmic C-tail. It may function as an integral membrane protein involved in cell-cell/matrix interactions, and may modulate intracellular calcium homoeostasis and other signal-transduction pathways. It plays a role in renal tubular development, and mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
...
Wikipedia