P-type primary ion transport ATPase
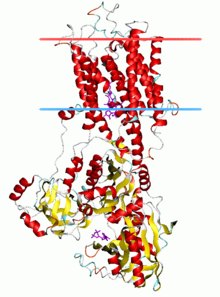
Calcium ATPase, E2-Pi state
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | E1-E2_ATPase | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00122 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR008250 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00139 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1su4 | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1su4 | ||||||||
| TCDB | 3.A.3 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 22 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 3b9b | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| Cation transporting ATPase, C-terminus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

crystal structure of the sr ca2+-atpase with bound amppcp
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Cation_ATPase_C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00689 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR006068 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1eul | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1eul | ||||||||
| TCDB | 3.A.3 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| Cation transporter/ATPase, N-terminus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
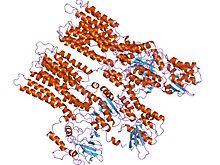
model of neurospora crassa proton atpase
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Cation_ATPase_N | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00690 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR004014 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1eul | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1eul | ||||||||
| TCDB | 3.A.3 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
The P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases, are a large group of evolutionarily related ion and lipid pumps that are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. P-type ATPases fall under the P-type ATPase (P-ATPase) Superfamily (TC# 3.A.3) which, as of early 2016, includes 20 different protein families. P-type ATPases are α-helical bundle primary transporters named based upon their ability to catalyze auto- (or self-) phosphorylation of a key conserved aspartate residue within the pump and their energy source, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E1 and E2.
Most members of this transporter superfamily catalyze cation uptake and/or efflux, however one subfamily (TC# 3.A.3.8) is involved in flipping phospholipids to maintain the asymmetric nature of the biomembrane.
Prominent examples of P-type ATPases are the sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+-ATPase), the plasma membrane proton pump (H+-ATPase), the proton-potassium pump (H+/K+-ATPase), and the calcium pump (Ca2+-ATPase).
The first P-type ATPase discovered was the Na+/K+-ATPase, which Nobel laureate Jens Christian Skou isolated in 1957. The Na+/K+-ATPase was only the first member of a large and still-growing protein family (see Swiss-Prot Prosite motif PS00154).
...
Wikipedia
