Oxaliplatin
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Eloxatin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607035 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Complete |
| Biological half-life | ~10 - 25 minutes |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.118 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
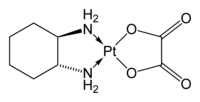
| Formula | C8H14N2O4Pt |
| Molar mass | 397.2858 g/mol |
|
|
|
Oxaliplatin, sold under the brand name Eloxatin, is a cancer medication used to treat colorectal cancer. Often it is used together with fluorouracil and folinic acid (leucovorin) in advanced cancer. It is given by injection into a vein.
Common side effects include numbness, feeling tired, nausea, diarrhea, and low blood cell counts. Other serious side effects include allergic reactions. Use in pregnancy is known to harm the baby. Oxaliplatin is in the platinum-based antineoplastic family of medications. It is believed to work by blocking the duplication of DNA.
Oxaliplatin was patented in 1976 and approved for medical use in 1996. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale cost in the developing world is 8.74 to 125.43 USD a vial. In the United Kingdom it costs the NHS 299.50 pounds per 100 mg dose.
Oxaliplatin is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, typically along with folinic acid and 5-fluorouracil in a combination known as FOLFOX. Oxaliplatin has been compared with other platinum compounds used for advanced cancers, such as cisplatin and carboplatin.
In clinical studies, oxaliplatin by itself has modest activity against advanced colorectal cancer. When compared with just 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid administered according to the de Gramont regimen, a FOLFOX4 regime produced no significant increase in overall survival, but did produce an improvement in progression-free survival, the primary end-point of the phase III randomized trial.
...
Wikipedia
