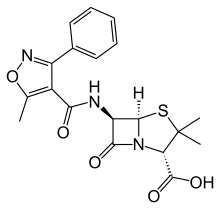
Oxacillin
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Bactocill |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | |
| MedlinePlus | a685020 |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.577 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H19N3O5S |
| Molar mass | 401.436 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Density | 1.49 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 686.8 °C (1,268.2 °F) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oxacillin sodium (trade name Bactocill) is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class developed by Beecham.
Oxacillin is a penicillinase-resistant β-lactam. It is similar to methicillin, and has replaced methicillin in clinical use. Other related compounds are nafcillin, cloxacillin, dicloxacillin, and flucloxacillin. Since it is resistant to penicillinase enzymes, such as that produced by Staphylococcus aureus, it is widely used clinically in the US to treat penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. However, with the introduction and widespread use of both oxacillin and methicillin, antibiotic-resistant strains called methicillin-resistant and oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA/ORSA) have become increasingly prevalent worldwide. MRSA/ORSA is treated using vancomycin.
Side effects include hypersensitivity and local reactions. In high doses, renal, hepatic, or nervous system effects can occur.
...
Wikipedia
