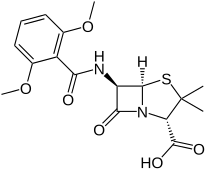
Methicillin
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
IV |
| ATC code | J01CF03 (WHO) QJ51CF03 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Not orally absorbed |
| Metabolism | hepatic, 20–40% |
| Biological half-life | 25–60 minutes |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
61-32-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6087 |
| DrugBank |
DB01603 |
| ChemSpider |
5862 |
| UNII |
Q91FH1328A |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL575 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.460 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H20N2O6S |
| Molar mass | 380.42 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
|
Meticillin (INN), also known as methicillin (USAN), is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It should not be confused with the antibiotic metacycline.
Meticillin was discovered in 1960.
Compared to other penicillins that face antimicrobial resistance due to β-lactamase, it is less active, can be administered only parenterally, and has a higher frequency of interstitial nephritis, an otherwise-rare adverse effect of penicillins. However, selection of meticillin depended on the outcome of susceptibility testing of the sampled infection, and since it is no longer produced, it is also not routinely tested for any more. It also served a purpose in the laboratory to determine the antibiotic sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus to other penicillins facing β-lactam resistance; this role has now been passed on to other penicillins, namely cloxacillin, as well as genetic testing for the presence of mecA gene by PCR.
At one time, meticillin was used to treat infections caused by certain gram-positive bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Meticillin is no longer effective against these organisms due to resistance.
Resistance to meticillin is conferred by activation of a new bacterial penicillin binding protein (PBP) mecA gene. This encodes protein PBP2a. PBP2a works in a similar manner to other PBPs, but it binds β-lactams with very low affinity, meaning they do not compete efficiently with the natural substrate of the enzyme and will not inhibit cell wall biosynthesis. Expression of PBPA2 confers resistance to all β-lactams.
...
Wikipedia
