Omphalocele
| Omphalocele | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q79.2 |
| ICD-9-CM | 756.72 |
| OMIM | 164750 |
| DiseasesDB | 23647 |
| MedlinePlus | 000994 |
| eMedicine | rad/483 |
| MeSH | D006554 |
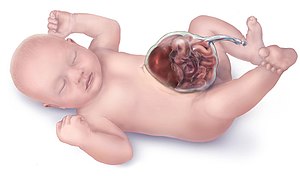
An omphalocele (British English: omphalocoele) is a rare abdominal wall defect in which the intestines, liver, and occasionally other organs remain outside of the abdomen in a sac because of a defect in the development of the muscles of the abdominal wall (exomphalos). Omphalocele occurs in 1/4,000 births and is associated with a high rate of mortality (25%) and severe malformations, such as cardiac anomalies (50%) and neural tube defect (40%). Approximately 15% of live-born infants with omphalocele have chromosomal abnormalities. About 30% of infants with an omphalocele have other congenital abnormalities.
The sac, which is formed from an outpouching of peritoneum, protrudes in the midline, through the umbilicus (navel).
It is normal for the intestines to protrude from the abdomen, into the umbilical cord, until about the tenth week of pregnancy, after which they return to inside the fetal abdomen.
The omphalocele can be mild, with only a small loop of intestines present outside the abdomen, or severe, containing most of the abdominal organs. In severe cases surgical treatment is made more difficult because the infant's abdomen is abnormally small, having had no need to expand to accommodate the developing organs.
Larger omphalocele are associated with a higher risk of cardiac defects.
An omphalocele is often detected through AFP screening or a detailed fetal ultrasound. Genetic counseling and genetic testing such as amniocentesis are usually offered during the pregnancy.
Caused by malrotation of the bowels while returning to the abdomen during development. Some cases of omphalocele are believed to be due to an underlying genetic disorder, such as Edward's syndrome (Trisomy 18) or Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13).
...
Wikipedia
