Northern Pacific Railroad Company
 |
|
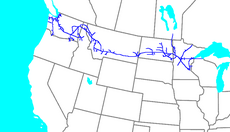
The Northern Pacific Railway system map
|
|

The former Northern Pacific Office Building
in Tacoma, Washington. |
|
| Reporting mark | NP |
|---|---|
| Locale |
Ashland, Wisconsin and Saint Paul, Minnesota to Seattle, Washington, Tacoma, Washington, and Portland, Oregon |
| Dates of operation | 1864–1970 |
| Successor |
Burlington Northern (later BNSF) |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Headquarters | Saint Paul, Minnesota |
The Northern Pacific Railway (reporting mark NP) was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest. It was approved by Congress in 1864 and given nearly forty million acres (62,000 sq mi; 160,000 km2) of land grants, which it used to raise money in Europe for construction.
Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former President Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in western Montana on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about 6,800 miles (10,900 km) of track and served a large area, including extensive trackage in the states of Idaho, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin. In addition, the NP had an international branch to Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The main activities were shipping wheat and other farm products, cattle, timber, and minerals; bringing in consumer goods, transporting passengers; and selling land.
The Northern Pacific was headquartered in Minnesota, first in Brainerd, then in Saint Paul. It had a tumultuous financial history; the NP merged with other lines in 1970 to form the Burlington Northern Railroad, which became BNSF Railway in 1996.
...
Wikipedia
