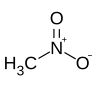
Nitromethane
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Nitromethane
|
|||
| Other names
Nitrocarbol
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
75-52-5 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:77701 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL276924 |
||
| ChemSpider |
6135 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.797 | ||
| KEGG |
C19275 |
||
| PubChem | 6375 | ||
| RTECS number | PA9800000 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| CH3NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 61.04 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless, oily liquid | ||
| Odor | Light, fruity | ||
| Density | 1.1371 g/cm3 (20 °C) | ||
| Melting point | −28.38 °C (−19.08 °F; 244.77 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 101.19 °C (214.14 °F; 374.34 K) | ||
| ca. 10 g/100 mL | |||
| Solubility | miscible in diethyl ether, acetone, ethanol | ||
| Vapor pressure | 28 mmHg (20°C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 17.2 in DMSO | ||
| -21.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3817 (20 °C) | ||
| Viscosity | 0.61 cP at 25 °C | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Flammable, harmful | ||
| Safety data sheet | See: data page | ||
| R-phrases | R5 R10 R22 | ||
| S-phrases | S41 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 35 °C (95 °F; 308 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 7.3%-? | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
940 mg/kg (oral, rat) 950 mg/kg (oral, mouse) |
||
|
LDLo (lowest published)
|
750 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 125 mg/kg (dog, oral) |
||
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
7087 ppm (mouse, 2 hr) 1000 ppm (monkey) 2500 ppm (rabbit, 12 hr) 5000 ppm (rabbit, 6 hr) |
||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 100 ppm (250 mg/m3) | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
none | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
750 ppm | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related nitro compounds
|
nitroethane | ||
|
Related compounds
|
methyl nitrite methyl nitrate |
||
| Supplementary data page | |||
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Nitromethane is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH
3NO
2. It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis, it is used widely in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, explosives, fibers, and coatings. Nitromethane is used as a fuel in various motorsports and hobbies, e.g. Top Fuel drag racing and miniature internal combustion engines in radio control, control line and free flight model aircraft.
Nitromethane is produced industrially by treating propane with nitric acid at 350–450 °C (662–842 °F). This exothermic reaction produces the four industrially significant nitroalkanes: nitromethane, nitroethane, 1-nitropropane, and 2-nitropropane. The reaction involves free radicals, including the alkoxyl radicals of the type CH3CH2CH2O, which arise via homolysis of the corresponding nitrite ester. These alkoxy radicals are susceptible to C—C fragmentation reactions, which explains the formation of a mixture of products.
It can be prepared in other methods that are of instructional value. The reaction of sodium chloroacetate with sodium nitrite in aqueous solution produces this compound:
...
Wikipedia