Nine Cantons
| Aden Protectorate | ||||||||||||||||
| محمية عدن | ||||||||||||||||
| Protectorate | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
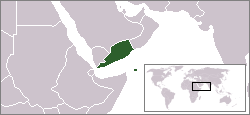
Location of the Aden Protectorate on the Arabian Peninsula.
|
||||||||||||||||
| Capital | none | |||||||||||||||
| Languages |
Arabic Persian English Ottoman Turkish |
|||||||||||||||
| Religion |
Islam Judaism Christianity |
|||||||||||||||
| Political structure | Protectorate | |||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||
| • | Initial treaty | 1874 | ||||||||||||||
| • | Federation formed | 11 February 1959 | ||||||||||||||
| • | Disestablished | 18 January 1963 | ||||||||||||||
| Area | 285,000 km² (110,039 sq mi) | |||||||||||||||
| Currency | Thaler | |||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Today part of |
|
|||||||||||||||
The Aden Protectorate (Arabic: محمية عدن Maḥmiyyat ‘Adan) was a British protectorate in southern Arabia which evolved in the hinterland of the port of Aden and in the Hadramaut following the conquest of Aden by Great Britain in 1839, and it continued until the 1960s. In 1940 it was divided for administrative purposes into the Western Protectorate and the Eastern Protectorate. Today the territory forms part of the Republic of Yemen.
What became known as the Aden Protectorate was initially informal arrangements of protection with nine tribes in the immediate hinterland of the port city of Aden:
British expansion into the area was designed to secure the important port that was, at the time, governed from British India. From 1874, these protection arrangements existed with the tacit acceptance of the Ottoman Empire that maintained suzerainty over Yemen to the north and the polities became known collectively as the "Nine Tribes" or the "Nine Cantons."
Beginning with a formal treaty of protection with the Mahra Sultanate of Qishn and Socotra in 1886, Britain embarked on a slow formalisation of protection arrangements that included over 30 major treaties of protection with the last signed only in 1954. These treaties, together with a number of other minor agreements, created the Aden Protectorate that extended well east of Aden to Hadhramaut and included all of the territory that would become South Yemen except for the immediate environs and port of the colonial capital, Aden.
...
Wikipedia