Neck of pancreas
| Pancreas | |
|---|---|
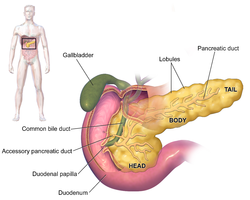
Anatomy of the pancreas
|
|
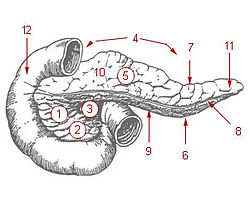
1: Head of pancreas
2: Uncinate process of pancreas 3: Pancreatic notch 4: Body of pancreas 5: Anterior surface of pancreas 6: Inferior surface of pancreas 7: Superior margin of pancreas 8: Anterior margin of pancreas 9: Inferior margin of pancreas 10: Omental tuber 11: Tail of pancreas 12: Duodenum |
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | Pancreatic buds |
| Artery | Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery, anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery, posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery, splenic artery |
| Vein | Pancreaticoduodenal veins, pancreatic veins |
| Nerve | Pancreatic plexus, celiac ganglia, vagus nerve |
| Lymph | Splenic lymph nodes, celiac lymph nodes and superior mesenteric lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Pancreas |
| Greek | Πάγκρεας (Pánkreas) |
| MeSH | A03.734 |
| TA | A05.9.01.001 |
| FMA | 7198 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide, all of which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing bicarbonate to neutralize acidity of chyme moving in from the stomach, as well as digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme. The pancreas is known as a mixed gland.
...
Wikipedia
