Mineralocorticoid
| Mineralocorticoid | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
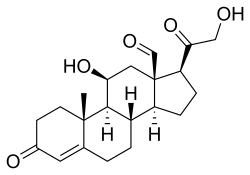
Aldosterone, the major endogenous mineralocorticoid.
|
|
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Corticosteroid; Mineralocorticosteroid |
| ATC code | H02AA |
| Biological target | Mineralocorticoid receptor |
| Chemical class | Steroids |
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are corticosteroids that influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary mineralocorticoid is aldosterone, notable for an aldehyde group at the 18 position.
The name mineralocorticoid derives from early observations that these hormones were involved in the retention of sodium, a mineral. The primary endogenous mineralocorticoid is aldosterone, although a number of other endogenous hormones (including progesterone and deoxycorticosterone) have mineralocorticoid function.
Aldosterone acts on the kidneys to provide active reabsorption of sodium and an associated passive reabsorption of water, as well as the active secretion of potassium in the principal cells of the cortical collecting tubule and active secretion of protons via proton ATPases in the lumenal membrane of the intercalated cells of the collecting tubule. This in turn results in an increase of blood pressure and blood volume.
Aldosterone is produced in the zona glomerulosa of the cortex of the adrenal gland and its secretion is mediated principally by angiotensin II but also by adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) and local potassium levels.
...
Wikipedia
