Methane gas
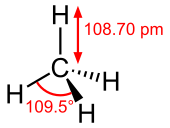 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Methane
|
|||
|
Systematic IUPAC name
Carbane (never recommended)
|
|||
Other names
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | B01450 | ||
| 1718732 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.739 | ||
| EC Number | 200-812-7 | ||
| 59 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Methane | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | PA1490000 | ||
| UN number | 1971 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| CH4 | |||
| Molar mass | 16.04 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density | 0.656 g/L (gas, 25 °C, 1 atm) 0.716 g/L (gas, 0 °C, 1 atm) 0.42262 g cm−3 (liquid, −162 °C) |
||
| Melting point | −182.5 °C; −296.4 °F; 90.7 K | ||
| Boiling point | −161.49 °C; −258.68 °F; 111.66 K | ||
| 22.7 mg L−1 | |||
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene, toluene, methanol, acetone | ||
| log P | 1.09 | ||
|
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
14 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
| -12.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Structure | |||
| Td | |||
| Tetrahedron | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 35.69 J K−1 mol−1 | |||
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
186.25 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−74.87 kJ mol−1 | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH |
−891.1 to −890.3 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | See: data page | ||
| GHS pictograms |  |
||
| GHS signal word | DANGER | ||
| H220 | |||
| P210 | |||
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|||
| R-phrases | R12 | ||
| S-phrases | (S2), S16, S33 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | −188 °C (−306.4 °F; 85.1 K) | ||
| 537 °C (999 °F; 810 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 4.4–17% | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related alkanes
|
|||
| Supplementary data page | |||
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Methane (US /ˈmɛθeɪn/ or UK /ˈmiːθeɪn/) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4 (one atom of carbon and four atoms of hydrogen). It is a group 14 hydride and the simplest alkane, and is the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an attractive fuel, though capturing and storing it poses challenges due to its gaseous state under normal conditions for temperature and pressure.
Natural methane is found both below ground and under the sea floor. When it reaches the surface and the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. The Earth's atmospheric methane concentration has increased by about 150% since 1750, and it accounts for 20% of the total radiative forcing from all of the long-lived and globally mixed greenhouse gases (these gases don't include water vapor which is by far the largest component of the greenhouse effect).
...
Wikipedia



