Mannose metabolism
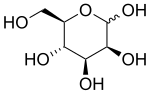
D-Mannopyranose
|
|
 Fischer projections
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
3458-28-4 |
|
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL469448 |
| ChemSpider |
17893 D-mannopyranose |
| 4650 | |
| MeSH | Mannose |
| PubChem | 18950 |
| UNII |
PHA4727WTP |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 180.16 g·mol−1 |
| -102.90·10−6 cm3/mol | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Mannose, packaged as the nutritional supplement "d-mannose", is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. Mannose is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation are associated with mutations in enzymes involved in mannose metabolism.
Mannose is not an essential nutrient; it can be produced in the human body from glucose, or converted into glucose. Mannose provides 2-5 kilocalories per gram. Mannose is partially excreted in the urine.
Mannose commonly exists as two different sized rings, the pyranose (six-membered) form and the furanose (five-membered) form. Each ring closure can have either an alpha or beta configuration at the anomeric position. The chemical rapidly undergoes isomerization among these four forms.
While much of the mannose used in glycosylation is believed to be derived from glucose, in cultured hepatoma (cancerous cells from the liver) cells, most of the mannose for glycoprotein biosynthesis comes from extracellular mannose, not glucose. Many of the glycoproteins produced in the liver are secreted into the bloodstream, so dietary mannose is distributed throughout the body.
Mannose is present in numerous glycoconjugates including N-linked glycosylation of proteins. C-Mannosylation is also abundant and can be found in collagen-like regions.
The digestion of many polysaccharides and glycoproteins yields mannose which is phosphorylated by hexokinase to generate mannose-6-phosphate. Mannose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose-6-phosphate, by the enzyme phosphomannose isomerase, and then enters the glycolytic pathway or is converted to glucose-6-phosphate by the gluconeogenic pathway of .
...
Wikipedia
