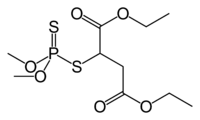
Malathion
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Diethyl 2-[(dimethoxyphosphorothioyl)sulfanyl]butanedioate
|
|
| Other names
2-(dimethoxyphosphinothioylthio) butanedioic acid diethyl ester
Malathion Carbofos Maldison Mercaptothion Ortho malathion |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
121-75-5 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:6651 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL1200468 |
| ChemSpider |
3864 |
| DrugBank |
DB00772 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.089 |
| KEGG |
D00534 |
| PubChem | 4004 |
| UNII |
U5N7SU872W |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H19O6PS2 | |
| Molar mass | 330.358021 |
| Appearance | Clear colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2.9 °C (37.2 °F; 276.0 K) |
| Boiling point | 156 to 157 °C (313 to 315 °F; 429 to 430 K) at 0.7 mmHg |
| 145 mg/L at 20 °C | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol and acetone; very soluble in ethyl ether |
| log P | 2.36 (octanol/water) |
| Pharmacology | |
| P03AX03 (WHO) QP53AF12 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 163 °C; 325 °F; 436 K (greater than) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
290 mg/kg (rat, oral) 190 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 570 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) |
|
LC50 (median concentration)
|
84.6 mg/m3 (rat, 4 hr) |
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
10 mg/m3 (cat, 4 hr) |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 15 mg/m3 [skin] |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 mg/m3 [skin] |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
250 mg/m3 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide of relatively low human toxicity. In the former USSR, it was known as carbophos, in New Zealand and Australia as maldison and in South Africa as mercaptothion.
Malathion is a pesticide that is widely used in agriculture, residential landscaping, public recreation areas, and in public health pest control programs such as mosquito eradication. In the US, it is the most commonly used organophosphate insecticide.
Malathion as a mixture with corn syrup was used in the 1980s in Australia and California to combat the Mediterranean fruit fly. In Canada and the US, malathion was sprayed in many cities to combat west Nile virus. Malathion was used over the last couple of decades on a regular basis during summer months to kill mosquitoes, but homeowners were allowed to exempt their properties if they chose. Today, Winnipeg is the only major city in Canada with an ongoing malathion adult-mosquito-control program.
Malathion is a cholinesterase inhibitor, a diverse family of chemicals that includes sarin and carbaryl. Upon uptake into the target organism, it binds irreversibly to several, random serine residues on the cholinesterase enzyme, with a peroxide as the leaving group. The resultant phosphoester group is strongly bound to the cholinesterase, and irreversibly deactivates the enzyme which leads to rapid build-up of acetylcholine at the synapse.
It is produced by the addition of dimethyl dithiophosphoric acid to diethyl maleate. The compound is chiral but is used as a racemate.
...
Wikipedia
