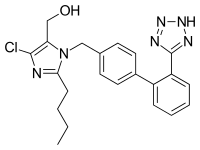
Losartan
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cozaar |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a695008 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | C09CA01 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25–35% |
| Protein binding | 99.7% (primarily albumin) |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2C9, CYP3A4) |
| Biological half-life | 1.5–2 hours |
| Excretion | Renal 13–25%, biliary 50–60% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
114798-26-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3961 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 590 |
| DrugBank |
DB00678 |
| ChemSpider |
3824 |
| UNII |
JMS50MPO89 |
| KEGG |
D08146 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:6541 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL191 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.110.555 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H23ClN6O |
| Molar mass | 422.91 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Losartan (rINN) /loʊˈsɑːrtən/ is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist drug used mainly to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It was the first angiotensin II antagonist to be marketed. Losartan potassium is marketed by Merck & Co. Inc. under the trade name Cozaar, and is available in generic form.
As with all angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1) antagonists, losartan is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may also delay progression of diabetic nephropathy and is associated with a positive clinical outcome in that regard. It is a suitable pharmacological agent for the reduction of renal disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and microalbuminuria (>30 mg/24 hours) or proteinuria (>900 mg/24 hours).
Although clinical evidence shows calcium channel blockers and thiazide-type diuretics are preferred first-line treatments for most patients (due to both efficacy and cost), an angiotensin II receptor antagonist such as losartan is recommended as first-line treatment in patients under the age of 55 who cannot tolerate an ACE inhibitor. The LIFE study demonstrated losartan was significantly superior to atenolol in the primary prevention of adverse cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction or stroke), with a significant reduction in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality for a comparable reduction in blood pressure. A study hints that losartan has a beneficial effect on by reversing age related dysfunction in maintaining normal blood pressure and cellular energy usage. The maximal effects on blood pressure usually occur within 3–6 weeks of starting losartan.
...
Wikipedia
