Klaipėda revolt
| Klaipėda Revolt | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Historical map of Klaipėda Region (Memelland) and the northern part of East Prussia |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
Lithuanian Riflemen's Union |
||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Gabriel Jean Petisné |
Ernestas Galvanauskas Vincas Krėvė-Mickevičius Jonas Polovinskas-Budrys Erdmonas Simonaitis |
||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Around 250 soldiers | Around 1400 men | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 2 killed | 12 killed | ||||||
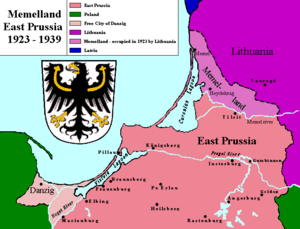
The Klaipėda Revolt took place in January 1923 in the Klaipėda Region (Memel Territory, Memelland). The region, located north of the Neman River, was detached from East Prussia, Germany by the Treaty of Versailles and became a mandate of the League of Nations. It was placed under provisional French administration until a more permanent solution could be worked out. Lithuania wanted to unite with the region (part of Lithuania Minor) due to its large Lithuanian-speaking minority of Prussian Lithuanians and major port of Klaipėda (Memel) – the only viable access to the Baltic Sea for Lithuania. As the Conference of Ambassadors favored leaving the region as a free city, similar to the Free City of Danzig, the Lithuanians organized and staged a revolt.
Presented as an uprising of the local population, the revolt met little resistance from either the German Police or the French Army. The rebels established a pro-Lithuanian administration, which petitioned to unite with Lithuania, citing the right of self-determination. The League of Nations accepted the fait accompli and the Klaipėda Region was transferred as an autonomous territory to the Republic of Lithuania on February 17, 1923. After prolonged negotiations a formal international agreement, the Klaipėda Convention, was signed in May 1924. The convention formally acknowledged Lithuania's sovereignty in the region and outlined its extensive legislative, judicial, administrative, and financial autonomy. The region remained part of Lithuania until March 1939 when it was transferred to Nazi Germany after the German ultimatum.
...
Wikipedia
