Incarcerated hernia
| Hernia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
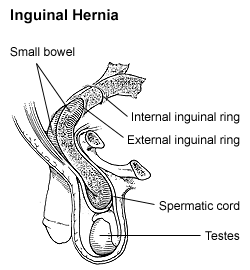
| Diagram of an indirect inguinal hernia (view from the side). | |
| Specialty | General surgery |
| Symptoms | Pain especially with coughing, bulging area |
| Complications | Bowel strangulation |
| Usual onset | < 1 year and > 50 years old (groin hernias) |
| Risk factors | Smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity, pregnancy, peritoneal dialysis, collagen vascular disease |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, medical imaging |
| Treatment | Observation, surgery |
| Frequency | 18.5 million (2015) |
| Deaths | 59,800 (2015) |
| Classification |
· ·
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Hernias come in a number of different types. Most commonly they involve the abdomen, specifically the groin. are most common of the inguinal type but may also be femoral. Other hernias include hiatus, incisional, and umbilical hernias. Symptoms are present in about 66% of people with groin hernias. This may include pain or discomfort especially with coughing, exercise, or going to the bathroom. Often it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying down. A bulging area may occur that becomes larger when bearing down. Groin hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the bowel is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness of the area. Hiatus or hiatal hernias often result in heartburn but may also cause chest pain or pain with eating.
Risk factors for the development of a hernia include: smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity, pregnancy, peritoneal dialysis, collagen vascular disease, and previous open appendectomy, among others. Hernias are partly genetic and occur more often in certain families. It is unclear if groin hernias are associated with heavy lifting. Hernias can often be diagnosed based on signs and symptoms. Occasionally medical imaging is used to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other possible causes. The diagnosis of hiatus hernias is often by endoscopy.
...
Wikipedia
