Hiatus hernia
| Hiatus hernia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology, general surgery |
| ICD-10 | K44, Q40.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 553.3, 750.6 |
| OMIM | 142400 |
| DiseasesDB | 29116 |
| MedlinePlus | 001137 |
| eMedicine | med/1012 radio/337 |
| MeSH | D006551 |
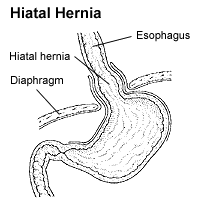
A hiatus hernia or hiatal hernia is a type of hernia in which the upper part of the stomach protrudes into the chest cavity through the esophageal hiatus in the diapragm due to a tear or weakness in the diaphragm.
The most common cause is obesity. The diagnosis is often by endoscopy or medical imaging.
A hiatus hernia may be improved by changes such as raising the head of the bed, weight loss, and adjusting eating habits. Medications that reduce gastric acid such as H2 blockers or proton pump inhibitors may help. If the symptoms do not improve with medications a surgical laparoscopic fundoplication may be an option.
Hiatal hernia has often been called the "great mimic" because its symptoms can resemble many disorders. For example, a person with this problem can experience dull pains in the chest, shortness of breath (caused by the hernia's effect on the diaphragm), heart palpitations (due to irritation of the vagus nerve), and swallowed food "balling up" and causing discomfort in lower esophagus until it passes on to stomach. Hiatus hernias often result in heartburn but may also cause chest pain or pain with eating.
In most cases however, a hiatal hernia does not cause any symptoms. The pain and discomfort that a patient experiences is due to the reflux of gastric acid, air, or bile. While there are several causes of acid reflux, it does happen more frequently in the presence of hiatal hernia.
...
Wikipedia
