Inguinal hernia
| Inguinal hernia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
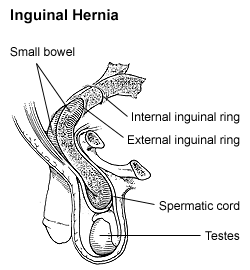
| Diagram of an indirect, scrotal inguinal hernia (median view from the left). | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈɪŋɡwᵻnəl ˈhɜːrniə/ |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | General surgery |
| ICD-10 | K40 |
| ICD-9-CM | 550 |
| DiseasesDB | 6806 |
| MedlinePlus | 000960 |
| eMedicine | med/2703 emerg/251 ped/2559 |
| MeSH | C06.405.293.249.437 |
An inguinal hernia is a protrusion of abdominal-cavity contents through the inguinal canal. Symptoms are present in about 66% of affected people. This may include pain or discomfort especially with coughing, exercise, or bowel movements. Often it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying down. A bulging area may occur that becomes larger when bearing down. Inguinal hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the intestine is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness of the area.
Risk factors for the development of a hernia include: smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity, pregnancy, peritoneal dialysis, collagen vascular disease, and previous open appendectomy, among others. Hernias are partly genetic and occur more often in certain families. It is unclear if inguinal hernias are associated with heavy lifting. Hernias can often be diagnosed based on signs and symptoms. Occasionally medical imaging is used to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other possible causes.
Groin hernias that do not cause symptoms in males do not need to be repaired. Repair, however, is generally recommended in females due to the higher rate of femoral hernias which have more complications. If strangulation occurs immediate surgery is required. Repair may be done by open surgery or by laparoscopic surgery. Open surgery has the benefit of possibly being done under local anesthesia rather than general anesthesia. Laparoscopic surgery generally has less pain following the procedure.
About 27% of males and 3% of females develop a groin hernia at some time in their life. Groin hernias occur most often before the age of one and after the age of fifty. Inguinal, femoral and abdominal hernias resulted in 51,000 deaths in 2013 and 55,000 in 1990.
...
Wikipedia
