Hypopyon
| Hypopyon | |
|---|---|
 |
|
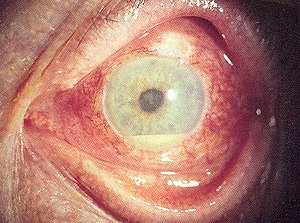
| Hypopyon seen as yellowish exudate in lower part of anterior chamber of eye | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-9-CM | 364.05 |
| DiseasesDB | 35115 |
Hypopyon is a medical condition involving inflammatory cells in the anterior chamber of the eye.
It is a leukocytic exudate, seen in the anterior chamber, usually accompanied by redness of the conjunctiva and the underlying episclera. It is a sign of inflammation of the anterior uvea and iris, i.e. iritis, which is a form of anterior uveitis. The exudate settles at the dependent aspect of the eye due to gravity.It can be sterile(in bacterial corneal ulcer) or not sterile(fungal corneal ulcer).
Hypopyon can be present in a corneal ulcer. Behcet's disease, endophthalmitis, panuveitis/panophthalmitis and adverse reactions to some drugs (such as rifabutin).
Hypopyon is also known as sterile pus, as it occurs due to the release of toxins and not by the actual invasion of pathogens. The toxins secreted by the pathogens mediate the outpouring of leukocytes that settle in the anterior chamber of the eye. Hypopyon is the only pus in the body that does not require any specific treatment as treatment of the underlying cause results in its resolution.
An inverse hypopyon is different from a standard hypopyon. Inverse hypopyon is seen after a pars plana vitrectomy with an insertion of silicone oil (as a replacement of the vitreous humour that has been removed in the operation; the silicone oil maintains internal tamponade). When the silicone oil emulsifies, it seeps into the anterior chamber and settles at the top of the anterior chamber. This is in contrast to hypopyon resulting from toxins where the leukocytes settle at the bottom of the anterior chamber. This is due to the effect of gravity, hence the name inverse hypopyon. .
...
Wikipedia
