Rifabutin
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mycobutin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a693009 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 85% |
| Protein binding | 85% |
| Metabolism | liver |
| Biological half-life | 28 to 62 hours (mean) |
| Excretion | kidney and fecal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.133.627 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
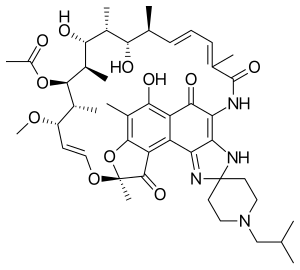
| Formula | C46H62N4O11 |
| Molar mass | 847.005 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Rifabutin (Rfb) is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and prevent and treat Mycobacterium avium complex. It is typically only used in those who cannot tolerate rifampin such as people with HIV/AIDS on antiretrovirals. For active tuberculosis it is used with other antimycobacterial medications. For latent tuberculosis it may be used by itself when the exposure was with drug-resistant TB.
Common side effects include abdominal pain, nausea, rash, headache, and low blood neutrophil levels. Other side effects include muscles pains and uveitis. While no harms have been found during pregnancy it has not been well studied in this population. Rifabutin is in the rifamycin family of medications. Its mechanism of action is not clear.
Rifabutin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1992. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 30 USD a month. In the United States a month of treatment is more than 200 USD.
Rifabutin is now recommended as first-line treatment for tuberculosis, but rifampicin is more widely used because of its cheaper cost.
Rifabutin is used in the treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex disease, a bacterial infection most commonly encountered in late-stage AIDS patients. Its main usefulness lies in the fact that it has lesser drug interactions than rifampicin; therefore HIV infected patients on HAART are usually given rifabutin for treatment of TB.
...
Wikipedia
