Hemiaminal
A hemiaminal (also carbinolamine) is a functional group or type of chemical compound that has a hydroxyl group and an amine attached to the same carbon atom: -C(OH)(NR2)-. R can be hydrogen or an alkyl group. Hemiaminals are intermediates in imine formation from an amine and a carbonyl by alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution.
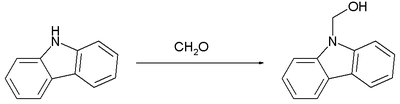
A hemiaminal is the first step in the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with an amine. Being one of the most reactive carbonyls, formaldehyde is well known to give carbinolamines. Illustrative is the reaction of the weakly basic secondary amine carbazole with formaldehyde.
As is typical with a secondary amine derivative, this carbinol converts readily to the methylene-linked bis(carbazole).
Those generated from primary amines are unstable to the extent that they have never been isolated and very rarely been observed directly. In a 2007 study a hemiaminal substructure trapped in the cavity of a host-guest complex was studied with a chemical half-life of 30 minutes. Because both amine and carbonyl group are isolated in a cavity, hemiaminal formation is favored due to a high forward reaction rate comparable to an intramolecular reaction and also due to restricted access of external base (another amine) to the same cavity which would favor elimination of water to the imine.
...
Wikipedia