Genvoya
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Vemlidy Genvoya (with elvitegravir, cobicistat and emtricitabine) Odefsey (with emtricitabine and rilpivirine) Descovy (with emtricitabine) |
| Routes of administration |
Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | ~80% |
| Biological half-life | 0.51 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (31.7%), urine (<1%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | GS-7340 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
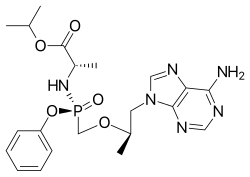
| Formula | C21H29N6O5P |
| Molar mass | 476.466 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Tenofovir alafenamide (INN/USAN; trade name Vemlidy) is a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor and a prodrug of tenofovir. It was developed by Gilead Sciences for use in the treatment of HIV infection and chronic hepatitis B, and is applied in the form of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate (TAF). Closely related to the commonly used reverse-transcriptase inhibitor tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), TAF has greater antiviral activity and better distribution into lymphoid tissues than that agent. Gilead was awarded FDA approval in November 2016 for the drug Vemlidy.
Gilead announced a phase 3 clinical trial evaluating a single-tablet regimen combining tenofovir alafenamide with cobicistat, emtricitabine and elvitegravir and developed a coformulation of the drug with cobicistat, emtricitabine and the protease inhibitor darunavir. In a 48-week study comparing elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil (trade name Stribild) to elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (trade name Genvoya), the results showed the newer drug to be noninferior to the established agent, but at much lower dosages and with lower incidence of adverse side effects such as impaired kidney function. The FDA approved the TAF-based treatment regimen for treatment of HIV-1 in November 2015. Genvoya is the first TAF-based regimen to receive approval.
...
Wikipedia
