Fraser syndrome
| Fraser syndrome | |
|---|---|
 |
|
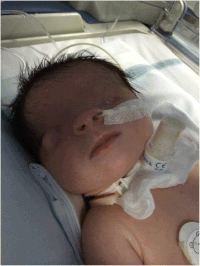
| Bilateral cryptophthalmos with microphthalmos in the left ocular globe and abnormal right ocular globe in a female infant with Fraser syndrome. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q87.0 |
| OMIM | 219000 |
| DiseasesDB | 32241 |
Fraser syndrome (also known as Meyer-Schwickerath's syndrome, Fraser-François syndrome, or Ullrich-Feichtiger syndrome) is an autosomal recessive congenital disorder. Fraser syndrome is named for the geneticist George R. Fraser, who first described the syndrome in 1962.
It is characterized by developmental defects including cryptophthalmos (where the eyelids fail to separate in each eye), and malformations in the genitals (such as micropenis, cryptorchidism or clitoromegaly).Congenital malformations of the nose, ears, larynx and renal system, as well as mental retardation, manifest occasionally.Syndactyly (fused fingers or toes) has also been noted.
The genetic background of this disease has been linked to a gene called FRAS1, which seems to be involved in skin epithelial morphogenesis during early development. It has also been associated with FREM2 and with GRIP1.
The diagnosis of this syndrome can be made on clinical examination and perinatal autopsy.
Koenig and Spranger (1986) noted that eye lesions are apparently nonobligatory components of the syndrome. The diagnosis of Fraser syndrome should be entertained in patients with a combination of acrofacial and urogenital malformations with or without cryptophthalmos. Thomas et al. (1986) also emphasized the occurrence of the cryptophthalmos syndrome without cryptophthalmos and proposed diagnostic criteria for Fraser syndrome. Major criteria consisted of cryptophthalmos, syndactyly, abnormal genitalia, and positive family history. Minor criteria were congenital malformation of the nose, ears, or larynx, cleft lip and/or palate, skeletal defects, umbilical hernia, renal agenesis, and mental retardation. Diagnosis was based on the presence of at least 2 major and 1 minor criteria, or 1 major and 4 minor criteria.
...
Wikipedia
