Flying the Hump
| The Hump | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Burma Campaign | |||||||
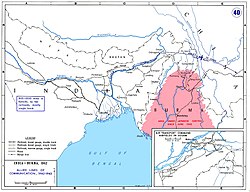 Allied lines of communication in Southeast Asia (1942–43). The Hump airlift is shown at upper right. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
|
||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
|||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 594 aircraft lost, missing, or written off 1,659 personnel killed or missing |
|||||||
The Hump was the name given by Allied pilots in the Second World War to the eastern end of the Himalayan Mountains over which they flew military transport aircraft from India to China to resupply the Chinese war effort of Chiang Kai-shek and the units of the United States Army Air Forces based in China. Creating an airlift presented the USAAF a considerable challenge in 1942: it had no units trained or equipped for moving cargo, and no airfields existed in the China Burma India Theater (CBI) for basing the large number of transports that would be needed. Flying over the Himalayas was extremely dangerous and made more difficult by a lack of reliable charts, an absence of radio navigation aids, and a dearth of information about the weather.
The task was initially given to the AAF's Tenth Air Force, and then to its Air Transport Command (ATC). Because the AAF had no previous airlift experience as a basis for planning, it assigned commanders who had been key figures in founding the ATC in 1941–1942 to build and direct the operation, which included former civilians with extensive executive experience operating civil air carriers.
Originally referred to as the "India-China Ferry", the successive organizations responsible for carrying out the airlift were the Assam-Burma-China Command (April–July 1942) and the India-China Ferry Command (July–December 1942) of the Tenth Air Force; and the Air Transport Command's India-China Wing (December 1942-June 1944) and India-China Division (July 1944-November 1945).
The operation began in April 1942, after the Japanese blocked the Burma Road, and continued daily to August 1945, when the effort began to scale down. It procured most of its officers, men, and equipment from the AAF, augmented by British, British-Indian Army, Commonwealth forces, Burmese labor gangs and an air transport section of the Chinese National Aviation Corporation (CNAC). Final operations were flown in November 1945 to return personnel from China.
...
Wikipedia
