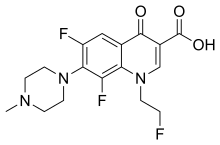
Fleroxacin
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.202.650 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H18F3N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 369.34 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fleroxacin is a quinolone. It is sold under the brand names Quinodis and Megalocin.
Fleroxacin is a bactericidal drug that inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Like other quinolones and fluoroquinolones the compound eradicates bacteria by interfering with DNA replication (bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair and recombination). Fleroxacin is active against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is especially active against Shigella species., Salmonella sp., Escherichia coli, Branhamella catarrhalis, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Yersinia enterocolitica, Serratia marcescens, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
After oral administration fleroxacin is rapidly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and shows a good bioavailability. The antibiotic is widely distributed throughout the body and in the different biological tissues. In many biologic specimens the levels of fleroxacin are similar to those in plasma, but in bile, nasal secretions, seminal fluid, lung, bronchial mucosa, and ovaries, the drug concentrations are 2-3 times higher than those in plasma. The serum elimination half-life, in subjects with normal renal function, is relatively long (9–12 hours), which permits once-daily dosing. Approximately the urinary excretion is 38% of an orally administered dose within 48 h, and in urine is possible detect 8.6% of the N-demethyl metabolite and 4.4% of the N-oxide metabolite. Fleroxacin can penetrate into milk of nursing women. As quinolones are known to induce arthropathy in juvenile animals, administration of the drug to breast-feeding women cannot be allowed.
...
Wikipedia
