Neisseria gonorrhoeae
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | |
|---|---|
 |
|
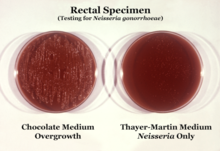
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae cultured on two different media types. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Betaproteobacteria |
| Order: | Neisseriales |
| Family: | Neisseriaceae |
| Genus: | Neisseria |
| Species: | N. gonorrhoeae |
| Binomial name | |
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Zopf, 1885 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Gonococcus Neisser 1879 |
|
Gonococcus Neisser 1879
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, also known as gonococci (plural), or gonococcus (singular), is a species of Gram-negative coffee bean-shaped diplococci bacteria responsible for the sexually transmitted infection gonorrhea.
N. gonorrhoeae was first described by Albert Neisser in 1879.
Neisseria species are fastidious Gram-negative cocci that require nutrient supplementation to grow in laboratory cultures. To be specific, they grow on chocolate agar with carbon dioxide. These cocci are facultatively intracellular and typically appear in pairs (diplococci), in the shape of coffee beans. Of the 11 species of Neisseria that colonize humans, only two are pathogens. N. gonorrhoeae is the causative agent of gonorrhea (also called "the clap") and is transmitted via sexual contact.
Neisseria is usually isolated on Thayer-Martin agar (or VPN agar)—an agar plate containing antibiotics (vancomycin, colistin, nystatin, and trimethoprim) and nutrients that facilitate the growth of Neisseria species while inhibiting the growth of contaminating bacteria and fungi. Further testing to differentiate the species includes testing for oxidase (all clinically relevant Neisseria species show a positive reaction) and the carbohydrates maltose, sucrose, and glucose test in which N. gonorrhoeae will oxidize only the glucose.
...
Wikipedia
