Euromaidan Revolution
| 2014 Ukrainian revolution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Euromaidan | |||
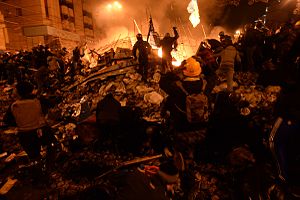
Protesters fighting government forces on Maidan Nezalezhnosti in Kiev on 18 February 2014.
|
|||
| Date | 18–23 February 2014 (5 days) | ||
| Location |
Mariinsky Park and Instytutska Street, Maidan Nezalezhnosti, Kiev, Ukraine 50°27′0″N 30°31′27″E / 50.45000°N 30.52417°E |
||
| Goals |
|
||
| Methods |
|
||
| Resulted in |
Euromaidan/Opposition victory
|
||
| Parties to the civil conflict | |||
|
|||
| Lead figures | |||
|
|
|||
| Number | |||
|
|||
| Casualties | |||
|
|||
|
Deaths: 113 Medical volunteer estimates |
|||
Euromaidan/Opposition victory
Kiev:
400,000–800,000 protesters
12,000 "self-defense sotnia"
Law enforcement in Kiev:
3,000–4,000 titushky
Pro-government/anti-EU demonstrations:
20,000–60,000 (Kiev)
40,000 (Kharkiv)
15,000 (Donetsk)
10,000 (Simferopol)
Deaths: 113
Injuries: 1,811
Ministry of Healthcare totals (16 April 2014 @6:00 LST)
The Ukrainian revolution of 2014 (also known as the Euromaidan Revolution or Revolution of Dignity; Ukrainian: Революція гідності, Revoliutsiia hidnosti) took place in Ukraine in February 2014, when a series of violent events involving protesters, riot police, and unknown shooters in the capital, Kiev, culminated in the ousting of Ukrainian President, Viktor Yanukovych. This was followed by a series of changes in Ukraine's sociopolitical system, including the formation of a new interim government, the restoration of the previous constitution, and a call to hold impromptu presidential elections within months.
After the breakup of the Soviet Union, Ukraine endured years of corruption, mismanagement, (years long) lack of economic growth, currency devaluation, and problems to secure funding from public markets. Successive Ukrainian governments in the 2000s sought a closer relationship with the European Union (EU). One of the measures meant to achieve this was an association agreement with the European Union, which would have provided Ukraine with funds in return for liberalising reforms. President Yanukovych announced his intention to sign the agreement, but ultimately refused to do so at the last minute. This sparked a wave of protests called the "Euromaidan" movement. During these protests Yanukovych signed a treaty and multibillion-dollar loan with Russia. The Ukrainian security forces cracked down on the protesters, further inflaming the situation and resulting in a series of violent clashes in the streets of Kiev. As tensions rose, Yanukovych fled to Russia and did not return.
...
Wikipedia
