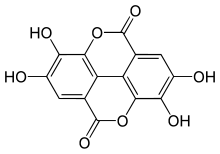
Ellagic acid
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
2,3,7,8-Tetrahydroxy-chromeno[5,4,3-cde]chromene-5,10-dione
|
|
| Other names
4,4′,5,5′,6,6′-Hexahydroxydiphenic acid 2,6,2′,6′-dilactone
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
476-66-4 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:4775 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL6246 |
| ChemSpider |
4445149 |
| DrugBank |
DB08468 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.827 |
| KEGG |
C10788 |
| PubChem | 5281855 |
| UNII |
19YRN3ZS9P |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C14H6O8 | |
| Molar mass | 302.197 g/mol |
| Density | 1.67 g/cm3 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Ellagic acid is a natural phenol antioxidant found in numerous fruits and vegetables. The antiproliferative and antioxidant properties of ellagic acid have prompted research into its potential health benefits. Ellagic acid is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid.
Plants produce ellagic acid from hydrolysis of tannins such as ellagitannin and geraniin.
Urolithins are microflora human metabolites of dietary ellagic acid derivatives
Ellagic acid was first discovered by chemist Henri Braconnot in 1831.Maximilian Nierenstein prepared this substance from algarobilla, dividivi, oak bark, pomegranate, myrabolams, and valonea in 1905. He also suggested its formation from galloyl-glycine by Penicillium in 1915.Löwe was the first person to synthesize ellagic acid by heating gallic acid with arsenic acid or silver oxide.
Ellagic acid is found in oaks species like the North American white oak (Quercus alba) and European red oak (Quercus robur).
The macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum produces ellagic acid.
Ellagic acid can be found in the medicinal mushroom Phellinus linteus.
...
Wikipedia
