Penicillium
| Penicillium | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Penicillium sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Phylum: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus: |
Penicillium Link (1809) |
| Type species | |
|
Penicillium expansum Link (1809) |
|
| Species | |
|
over 300 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Floccaria Grev. (1827) |
|
over 300
List of Penicillium species
Floccaria Grev. (1827)
Aspergilloides Dierckx (1901)
Walzia Sorokin (1871)
Pritzeliella Henn. (1903)
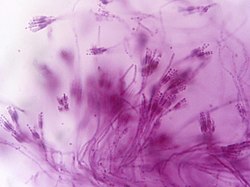
Penicillium (/ˌpɛnɪˈsɪliəm/) is a genus of ascomycetous fungi of major importance in the natural environment as well as food and drug production.
Some members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria inside the body. Other species are used in cheesemaking. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi (10th edition, 2008), the widespread genus contains over 300 species.
The genus was first described in the scientific literature by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in his 1809 work Observationes in ordines plantarum naturales, writing "Penicillium. Thallus e floccis caespitosis septatis simplicibus aut ramosis fertilibus erectis apice penicillatis", where penicillatis referred to "pencil-like" (referring to a Camel's hair pencil brush. Link included three species—P. candidum, P. expansum, and P. glaucum—all of which produced a brush-like conidiophore (asexual fruiting structure). The common apple rot fungus P. expansum was selected as the type species.
...
Wikipedia
