EU customs zone
|
European Union Customs Union
|
|
|---|---|
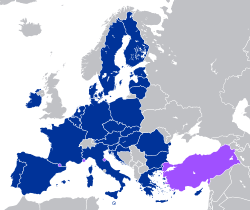
EU member states (including participating member state territories which are not part of the EU)
Non-EU states which participate in the customs union, or are in bilateral customs unions with the EU
|
|
| Policy of |
|
| Type | Customs union |
| Membership |
29 member states
3 states with bilateral agreements
|
| Establishment | 1958 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
5,200,000 km2 (2,000,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 2014 estimate
|
585,000,000 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2014 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$19.6 trillion |
| GDP (nominal) | 2014 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$19.2 trillion |
The European Union Customs Union (EUCU) is a customs union which consists of all the member states of the European Union (EU), Monaco, and some territories of the United Kingdom which are not part of the EU (Akrotiri and Dhekelia, Bailiwick of Guernsey, Bailiwick of Jersey, and the Isle of Man). Some territories within the EU do not participate in the customs union, usually as a result of their geographic circumstances. Besides the EUCU, the EU, through separate agreements, is in customs unions with Andorra, San Marino, and Turkey, with the exceptions of certain goods.
The customs union is a principal condition of the European Economic Community, established in 1958, and now succeeded by the European Union. No customs duties are levied on goods travelling within the customs union and—unlike a free trade area—members of the customs union impose a common external tariff on all goods entering the union. One of the consequences of the customs union is that the European Union negotiates as a single entity in international trade deals such as the World Trade Organisation, instead of individual member states negotiating for themselves.
Monaco and the British territories of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey are integral parts of the EU's customs territory.
![]() Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia
...
Wikipedia
