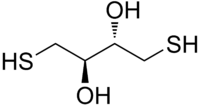
Dithioerythritol
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
(2R,3S)-1,4-Bis(sulfanyl)butane-2,3-diol
|
|
| Other names
(2R,3S)-1,4-Dimercaptobutane-2,3-diol (no longer recommended)
2,3-Dihydroxybutane-1,4-dithiol Erythro-2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-butanedithiol Erythro-1,4-dimercapto-2,3-butanediol Cleland's reagent (also used for DTT) |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.271 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H10O2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 154.253 g/mol |
| Melting point | 82 to 84 °C (180 to 183 °F; 355 to 357 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Dithioerythritol (DTE) is a sulfur containing sugar derived from the corresponding 4-carbon monosaccharide erythrose. It is an epimer of dithiothreitol (DTT). The molecular formula for DTE is C4H10O2S2.
Like DTT, DTE makes an excellent reducing agent, although its standard reduction potential is not quite as negative, i.e., DTE is slightly less effective at reducing than DTT, presumably because the lesser steric repulsion of its OH groups makes the cyclic disulfide-bonded form of DTE less stable compared to that of DTT. In DTT, these hydroxyl groups are cis to each other, whereas they are trans to each other in DTE.
...
Wikipedia
