Dimethylol ethylene urea
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Dimethylol ethylene urea
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.786 |
| EC Number | 205-264-2 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| (C2H2N2(CH2OH)2)CO | |
| Molar mass | 146.14g/mol |
| Appearance | White resin |
| Melting point | 161 to 163 °C (322 to 325 °F; 434 to 436 K) |
| Boiling point | 342.6±27 ℃ |
| 72g/L H2O at 25 ℃ | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Dimethylol ethyleneurea is an organic compound derived from formaldehyde and urea. It is a colourless solid that is used for treating cellulose-based heavy fabrics to inhibit wrinkle formation. Dimethylol ethylene urea (DMEU) bonds with the hydroxyl groups present in long strain cellulose chains and prevents the formation hydrogen bonding between the chains, the primary cause of wrinkling.
Wrinkles form in cotton fabrics due to the free hydroxyl groups. Cotton is a form of cellulose chains linked to form firm three-dimensional structures that offer both tensile strength and flexibility due to their carbon-carbon and carbon-oxygen bond based backbone. Since cellulose is composed of glucose units, cyclic carbohydrate molecules, cellulose has free hydroxyl groups (-OH) projecting from each monomeric subunit. These hydroxyl groups tend form hydrogen-bonds to neighboring hydroxyl groups. When the fabric is stressed either by heat or pressure, the original hydrogen bonds in the cotton fabric break and reform with nearby atoms at random. This re-forming of the hydrogen bonds, known as cross linking, is the reason for wrinkles, or creases, in the fabric. DMEU works to prevent these wrinkles by covalently bonding to two free hydroxyl groups in the fabric through a dehydration reaction that is not as easily broken as the hydrogen bond before treatment. 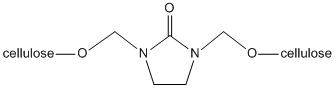
As seen in the figure, this formation of a C-O bond through a dehydration reaction (loss of water) allows the fabric to be bleached and heated to reasonable temperatures without fear of breaking the C-O bonds formed.
DMEU is applied industrially to the fabric after all the creases desired for design are in place. The fabric is heated and a DMEU resin is slathered on to the fabric. Depending on the procedure, the residue may contain metal catalysts or acid catalysts to help with the reaction.
The production of DMEU is through the condensation of formaldehyde with ethylene urea:
The reaction proceeds around 200 °C but this temperature can be brought down to around 70 °C in the presence of an acid catalyst.
Before the development of DMEU, formaldehyde and its derivatives were used as anti-wrinkle agents. These agents could successfully inhibit wrinkle formation. After contact with hydroochlorate bleaches at high temperatures, however, the treated fabric released hydrochloric acid, which degraded the fabric. Additionally, formaldehyde evaporates easily and is pungent. A search for stabler alternatives to formaldehyde led to dimethylol formaldehyde derivatives such as DMEU.
...
Wikipedia
