Dimanganese decacarbonyl
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
bis(pentacarbonylmanganese)(Mn—Mn)
|
|
| Other names
Manganese carbonyl
Decacarbonyldimanganese |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
10170-69-1 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider |
451751 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.392 |
| PubChem | 517769 |
| RTECS number | GG0300000 |
| UNII |
85SI7K7FWW |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10O10Mn2 | |
| Molar mass | 389.98 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow crystals |
| Density | 1.750 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 154 °C (309 °F; 427 K) |
| Boiling point | sublimes 60 °C (140 °F; 333 K) at 0.5 mm Hg |
| insoluble | |
| Structure | |
| 0 D | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | CO source |
| R-phrases | 23/24/25 |
| S-phrases | 22-26-36/37/39-45 |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Re2(CO)10 Co2(CO)8 Fe3(CO)12 Fe2(CO)9 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Dimanganese decacarbonyl is the chemical compound with the formula Mn2(CO)10. This metal carbonyl is an important reagent in the organometallic chemistry of manganese.
The compound was first prepared in low yield by the reduction of manganese iodide with magnesium under CO. A more efficient preparation entails reduction of anhydrous MnCl2 with sodium benzophenone ketyl under 200 atmospheres of CO. The availability of inexpensive methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl ("MMT") has led to a low pressure route to Mn2(CO)10.
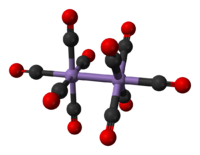
Mn2(CO)10 has no bridging CO ligands: it can be described (CO)5Mn-Mn(CO)5. There are two kinds of CO ligands; one CO on each Mn is coaxial with the Mn-Mn bond (293 pm), and four on each manganese that are perpendicular to it (equatorial). In the stable rotamer, the two Mn(CO)5 subunits are staggered. The overall molecule thus belongs to the point group D4d, which is an uncommon symmetry.
Mn2(CO)10 is air stable as a crystalline solid, but solutions require Schlenk techniques. It finds limited use in organic synthesis. Characteristic reactions:
The anion is a versatile nucleophile. Protonation gives the hydride [HMn(CO)5], and methylation gives [(CH3)Mn(CO)5].
Mn2(CO)10 is a volatile source of a metal and a source of CO.
...
Wikipedia
