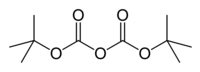
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Di-t-butyl dicarbonate
|
|
| Other names
Di-tert-butyl pyrocarbonate
Boc anhydride Boc2O |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.021 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H18O5 | |
| Molar mass | 218.25 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless solid or oil |
| Density | 0.95 g·cm−3 |
| Melting point | 22 to 24 °C (72 to 75 °F; 295 to 297 K) |
| Boiling point | 56 to 57 °C (133 to 135 °F; 329 to 330 K) (0.5 mmHg) |
| Insol | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in most organic solvents |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Very toxic on inhalation T+, LC50 = 100 mg/m3 (4 hr, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Ethyl chloroformate Phosgene Diethyl pyrocarbonate Dimethyl dicarbonate |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. Since this compound can be regarded formally as the acid anhydride derived from a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) group, it is commonly referred to as "Boc anhydride." This pyrocarbonate reacts with amines to give N-tert-butoxycarbonyl or so-called Boc derivatives. These carbamate derivatives do not behave as amines, which allows certain subsequent transformations to occur that would be incompatible with the amine functional group. The Boc group can later be removed from the amine using moderately strong acids (e.g., trifluoroacetic acid). Thus, Boc serves as a protective group, for instance in solid phase peptide synthesis. Boc-protected amines are unreactive to most bases and nucleophiles, allowing for the use of the fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl group (Fmoc) as an orthogonal protecting group.
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is inexpensive, so it is usually purchased. Classically, this compound is prepared from tert-butanol, carbon dioxide, and phosgene, using DABCO as a base:
This route is currently employed commercially by manufacturers in China and India. European and Japanese companies use the reaction of sodium tert-butoxide with carbon dioxide, catalysed by p-toluenesulfonic acid or methanesulfonic acid. This process involves a distillation of the crude material yielding a very pure grade.
...
Wikipedia

