D-penicillamine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cuprimine, Cuprenyl, Depen, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Variable |
| Metabolism | liver |
| Biological half-life | 1 hour |
| Excretion | kidney |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.136 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
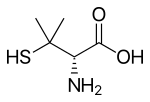
| Formula | C5H11NO2S |
| Molar mass | 149.212 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Penicillamine, sold under the trade names of Cuprimine among others, is a medication primarily used for the treatment of Wilson's disease. It is also used for people with kidney stones who have high urine cystine levels, rheumatoid arthritis, copper poisoning, and lead poisoning. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include rash, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, and low blood white blood cell levels. Other serious side effects include liver problems, obliterative bronchiolitis, and myasthenia gravis. It is not recommended in people with lupus erythematosus. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Penicillamine works by binding heavy metals such that they can be removed from the body in the urine.
Penicillamine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1970. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 0.55 to 1.20 USD a dose. In the United States treatment costs more than 200 USD per month.
It is used as a chelating agent:
Penicillamine can be used as a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) to treat severe active rheumatoid arthritis in patients who have failed to respond to an adequate trial of conventional therapy, although it is rarely used today due to availability of TNF inhibitors and other agents, such as and tofacitinib. Penicillamine works by reducing numbers of T-lymphocytes, inhibiting macrophage function, decreasing IL-1, decreasing rheumatoid factor, and preventing collagen from cross-linking.
...
Wikipedia
