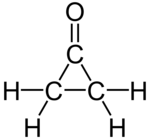
Cyclopropanone
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
cyclopropanone
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C3H4O | |
| Molar mass | 56.06326 |
| Density | 0.867 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Melting point | −90 °C (−130 °F; 183 K) |
| Boiling point | 50 to 53 °C (122 to 127 °F; 323 to 326 K) at 22 mmHg |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Cyclopropanone is an organic compound with molecular formula C3H4O consisting of a cyclopropane carbon framework with a ketone functional group. The parent compound is labile with melting point −90 °C and has been prepared by reaction of ketene with diazomethane at −145 °C. Derivatives of cyclopropanone are of some interest to organic chemistry.
In organic synthesis the use of cyclopropanone itself is substituted by that of synthons like acetals cyclopropanone ethyl hemiacetal or cyclopropanone ethyl trimethylsilyl acetal.
Cyclopropanones are intermediates in the Favorskii rearrangement with cyclic ketones where carboxylic acid formation is accompanied by ring-contraction.
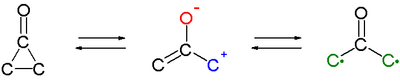
An interesting feature of cyclopropanones is that they react as 1,3-dipoles in cycloadditions for instance with cyclic dienes such as furan. An oxyallyl intermediate or valence tautomer (formed by cleavage of the C2-C3 bond) is suggested as the active intermediate or even a biradical structure (compare to the related trimethylenemethane).
...
Wikipedia