Cavernous sinuses
| Cavernous sinus | |
|---|---|
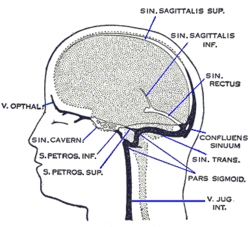
Cavernous sinus (center, labeled "SIN. CAVERN.")
|
|
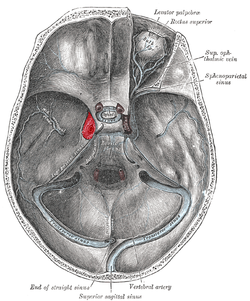
The sinuses at the base of the skull. Cavernous sinus labeled in red
|
|
| Details | |
| Source | middle cerebral vein, sphenoparietal sinus, superior ophthalmic vein, Inferior ophthalmic vein |
| Drains to | inferior petrosal sinus, superior petrosal sinus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sinus cavernosus |
| MeSH | A07.231.908.224 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
s_12/12738628 |
| TA | A12.3.05.116 |
| FMA | 50772 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The cavernous sinus within the human head, is a true dural venous sinus (not a venous plexus) creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structures within the lateral wall of the lateral sellar compartment:
Structures passing through the medial portion of the lateral sellar compartment:
Tributaries:
The sinus may be joined by several anastomoses across the midline. The cavernous sinus receives blood via the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins through the superior orbital fissure and from superficial cortical veins, and is connected to the basilar plexus of veins posteriorly. The internal carotid artery (carotid siphon), and cranial nerves III, IV, V (branches V1 and V2) and VI all pass through this blood filled space. Infection from the face may reach the cavernous sinus through its many anastomotic connections, with severe consequences. The cavernous sinus drains by two larger channels, the superior and inferior , ultimately into the internal jugular vein via the sigmoid sinus, also draining with emissary vein to pterygoid plexus.
Each cavernous sinus (one for each hemisphere of the brain) contains the following:
Unlike the nerves listed above, the abducens nerve (CN VI) does not run within the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus; rather, it runs through the middle of the sinus alongside the internal carotid artery.
These nerves, with the exception of CN V2, pass through the cavernous sinus to enter the orbital apex through the superior orbital fissure. The maxillary nerve, division V2 of the trigeminal nerve travels through the lower portion of the sinus and exits via the foramen rotundum.
A mnemonic exists to remember the orientation of the vertical and horizontal content of the sinus: O TOM CAT. (OTOM are the lateral wall contents from superior to inferior; CAT are the horizontal contents from medial to lateral)
...
Wikipedia
