Internal carotid
| Internal carotid artery | |
|---|---|
|
|

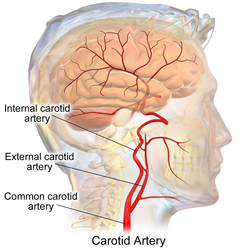
Arteries of the neck. The internal carotid arteries arise from the common carotid arteries - labeled Common caroti on the figure.
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | 3. aortic arch |
| Source | Common carotid artery |
| Branches | Ophthalmic, anterior choroidal, anterior cerebral, middle cerebral and posterior communicating artery |
| Vein | Internal jugular vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria carotis interna |
| MeSH | A07.231.114.186.200.230 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
Internal carotid artery |
| TA | A12.2.06.001 |
| FMA | 3947 |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
The internal carotid artery is a major paired artery, one on each side of the head and neck, in human anatomy. They arise from the common carotid arteries where these bifurcate into the internal and external carotid arteries at cervical vertebral level 3 or 4; the internal carotid artery supplies the brain, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as face, scalp, skull, and meninges.
Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". However, in clinical settings, the classification system of the internal carotid artery usually follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier—C1 cervical, C2 petrous, C3 lacerum, C4 cavernous, C5 clinoid, C6 ophthalmic, and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nomenclature remains in widespread use by neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists and neurologists. The segments are subdivided based on anatomical and microsurgical landmarks and surrounding anatomy, more than angiographic appearance of the artery. An alternative embryologic classification system proposed by and colleagues is invaluable when it comes to explanation of many internal carotid artery variants. An older clinical classification, based on pioneering work by Fischer, is mainly of historical significance.
The segments of the internal carotid artery are as follows:
Mnemonic for branches in skull: Please Let Children Consume Our Candy (first letter for each branch, in order).
The internal carotid artery is a terminal branch of the common carotid artery; it arises around the level of the fourth cervical vertebra when the common carotid bifurcates into this artery and its more superficial counterpart, the external carotid artery.
The cervical segment, or C1, or cervical part of the internal carotid, extends from the carotid bifurcation until it enters the carotid canal in the skull anterior to the jugular foramen.
...
Wikipedia
