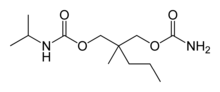
Carisoprodol
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Soma, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682578 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | M03BA02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 60% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2C19-mediated) |
| Metabolites | Meprobamate |
| Onset of action | Rapid |
| Biological half-life | 2 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
78-44-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 2576 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7610 |
| DrugBank |
DB00395 |
| ChemSpider |
2478 |
| UNII |
21925K482H |
| KEGG |
D00768 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:3419 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1233 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.017 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H24N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 260.33 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Carisoprodol, marketed under the brand name Soma among others, is a prescription drug marketed since 1959. It is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant of the carbamate class and produces all the effects associated with barbiturates. It is a prodrug and is both structurally and pharmacologically related to meprobamate. The major metabolic pathway of carisoprodol involves its conversion to meprobamate, a barbiturate-like drug.
In the United States, Carisoprodol is a Schedule IV controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. The diversion and abuse of the drug increased in the last decade. It is manufactured and marketed in the U.S. by Meda Pharmaceuticals and as of 2015[update], the cost for a typical course of the medication was less than US$25.
The usual dose of 350 mg is unlikely to engender prominent side effects other than somnolence, and mild to significant euphoria or dysphoria, but the euphoria is generally short lived. The medication is well tolerated and without adverse effects in the majority of patients for whom it is indicated. In some patients, however, and/or early in therapy, carisoprodol can have the full spectrum of sedative side effects and can impair the patient's ability to operate a firearm, motor vehicles, and other machinery of various types, especially when taken with medications containing alcohol, in which case an alternative medication would be considered. The intensity of the side effects of carisoprodol tends to lessen as therapy continues, as is the case with many other drugs.
The interaction of carisoprodol with essentially all opioids, and other centrally acting analgesics, but especially those of the codeine-derived subgroup of the semisynthetic class (codeine, ethylmorphine, dihydrocodeine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, nicocodeine, benzylmorphine, the various acetylated codeine derivatives including acetyldihydrocodeine, dihydroisocodeine, nicodicodeine and others) which allows the use of a smaller dose of the opioid to have a given effect, is useful in general and especially where skeletal muscle injury and/or spasm is a large part of the problem. The potentiation effect is also useful in other pain situations and is also especially useful with opioids of the open-chain class, such as methadone, levomethadone, ketobemidone, phenadoxone and others. In recreational drug users, deaths have resulted from carelessly combining overdoses of hydrocodone and carisoprodol. Another danger of misuse of carisoprodol and opiates is the potential to aspirate while unconscious.
...
Wikipedia
