Levomethadone
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration |
Oral, IV, IM, SC, IT |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | High |
| Protein binding | 60-90% |
| Biological half-life | ~18 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.120.592 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
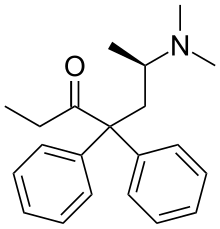
| Formula | C21H27NO |
| Molar mass | 309.445 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Levomethadone (INN; L-Polamidon, L-Polamivet, Levadone, Levothyl), or levamethadone, is a synthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive which is marketed in Europe and is used for pain management and in opioid maintenance therapy. In addition to being used as a pharmaceutical drug itself, levomethadone, or R-(−)-methadone, is the active enantiomer of methadone, having approximately 50x the potency of the S-(+)-enantiomer as well as greater μ-opioid receptor selectivity. Accordingly, it is about twice as potent as methadone by weight and its effects are virtually identical in comparison. In addition to its activity at the opioid receptors, levomethadone has been found to act as a weak competitive antagonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor complex and as a potent noncompetitive antagonist of the α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine (nACh) receptor.
There is now an asymmetric synthesis available to prepare both levomethadone [R-(−)-methadone] and dextromethadone [S-(+)-methadone].
...
Wikipedia
