Cardiac transplantation
| Heart transplantation | |
|---|---|
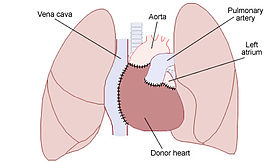
Diagram illustrating the placement of a donor heart in an orthotopic procedure. Notice how the back of the patient's left atrium and great vessels are left in place.
|
|
| Specialty | cardiology |
| ICD-9-CM | 37.51 |
| MeSH | D016027 |
| MedlinePlus | 003003 |
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. As of 2016, the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart (with or without transplantation of a lung or lungs; a cadaveric donor cardiectomy) from a recently deceased organ donor (the cadaveric allograft), and implant it into the patient. The patient's own heart is either removed (the cardiectomy for the recipient) and replaced with the donor heart (orthotopic procedure) or, much less commonly, the recipient's diseased heart is left in place to support the donor heart (heterotopic, or "piggyback," transplant procedure). Approximately 3500 heart transplants are performed every year in the world, more than half of which occur in the US. Post-operation survival periods average 15 years. Heart transplantation is not considered to be a cure for heart disease, but a life-saving treatment intended to improve the quality of life for recipients.
One of the first mentions of the possibility of heart transplantation was by American medical researcher Simon Flexner, who declared in a reading of his paper on “Tendencies in Pathology” in the University of Chicago in 1907 that it would be possible in the then-future for diseased human organs substitution for healthy ones by surgery — including arteries, stomach, kidneys and heart.
Not having a human donor heart available, James D. Hardy of the University of Mississippi Medical Center transplanted the heart of a chimpanzee into the chest of a dying Boyd Rush in the early morning of Jan. 24, 1964. Hardy used a defibrillator to shock the heart to restart beating. This heart did beat in Rush's chest for 60 to 90 minutes (sources vary), and then Rush died without regaining consciousness. Although Hardy was a respected surgeon who had performed the world's first human-to-human lung transplant a year earlier, author Donald McRae states that Hardy could feel the "icy disdain" from fellow surgeons at the Sixth International Transplantation Conference several weeks after this attempt with the chimpanzee heart. Hardy had been inspired by the limited success of Keith Reemtsma at Tulane University in transplanting chimpanzee kidneys into human patients with kidney failure. The consent form Hardy asked Rush's step sister to sign did not include the possibility that a chimpanzee heart might be used, although Hardy stated that he did include this in verbal discussions.
...
Wikipedia
