Canis lupus variabilis
| Great Plains wolf | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Illustration based on a description by Edward Alphonso Goldman | |
|
Extinct (1926)
|
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Canis |
| Species: | C. lupus |
| Subspecies: | †C. l. nubilus |
| Trinomial name | |
|
Canis lupus nubilus Say, 1823 |
|
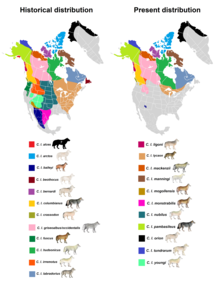 |
|
| Historical and present range of gray wolf subspecies in North America | |
| Synonyms | |
|
* variabilis (Wied-Neuwied, 1841) |
|
* variabilis (Wied-Neuwied, 1841)
The Great Plains wolf (Canis lupus nubilus), also known as the buffalo wolf or loafer, is an extinct subspecies of gray wolf with a distribution that once extended throughout the Great Plains from southern Manitoba and Saskatchewan southward to northern Texas. The last one was extirpated in 1926. They were described as a large, light-colored wolf but with black and white varying between individual wolves, with some all white or all black. The Native Americans of North Dakota told of how only three of these wolves could bring down any sized buffalo.
This wolf was first recorded in 1823 by the naturalist Thomas Say in his writings on Major Stephen Long's expedition to the Great Plains. Say was the first person to document the difference between a "prairie wolf" (coyote) and on the next page of his journal a wolf which he named Canis nubilus. He described one of these wolves that had been caught in a trap:
Canis nubilus. Dusky, the hair cinereous at base, then brownish-black then gray, then black; the proportion of black upon the hairs, is so considerable, as to give to the whole animal a much darker colour, than the darkest of the latrans, but the gray of the hairs combining with the black tips, in the general effect produce a mottled appearance; the gray colour predominates on the lower part of the sides; ears short, deep brownish-black, with a patch of gray hair on the anterior side within; muzzle blackish above; superior lifjs, anterior to the canine teeth, gray; inferior jaw at tip and extending in a narrowed line backwards, nearly to the origin of the neck, gray; beneath dusky ferruginous, greyish with long hair between the hind thighs, and with a large white spot on the breast; the ferruginous colour is very much narrowed on the neck, but is dilated on the lower part of the cheeks; legs brownish- black, with but a slight admixture of gray hairs, excepting on the anterior edge of the hind thighs, and the lower edgings of the toes, where the gray predominates; the tail is short, fusiform, a little tinged with ferruginous, black above near the base and at tip, the tip of the trunk hardly attaining to the os calcis; the longer hairs of the back, particularly over the shoulders, resemble a short sparse mane.....The aspect of this animal is far more fierce and formidable than either the common red wolf, or the prairie wolf, and is of a more robust form.
...
Wikipedia
