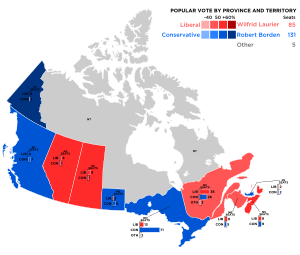
Canadian federal election, 1911
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
221 seats in the 12th Canadian Parliament 111 seats needed for a majority |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Canadian federal election of 1911 was held on September 21 to elect members of the Canadian House of Commons of the 12th Parliament of Canada.
The central issue was Liberal support for a proposed treaty with the US to lower tariffs. The Conservatives denounced it because it threatened to weaken ties with Britain and submerge the Canadian economy and Canadian identity into its big neighbour. The Conservatives won, and Robert Borden became prime minister. The idea of a Canadian Navy was also an issue. The election ended 15 years of government by the Liberal Party of Wilfrid Laurier.
The Liberal government was caught up in a debate over the naval arms race between the British Empire and Germany. Laurier attempted a compromise by starting up the Canadian Navy (now the Royal Canadian Navy), but this failed to appease either the French or English Canadians; the former who refused giving any aid, while the latter suggested sending money directly to Britain. After the election, the Conservatives drew up a bill for naval contributions to the British, but it was held up by a lengthy Liberal filibuster before being passed by invoking closure, then it was struck down by the Liberal-controlled Senate.
Many English Canadians in British Columbia and the Maritimes felt that Laurier was abandoning Canada's traditional links to their mother country, Great Britain. On the other side, Quebec nationalist Henri Bourassa, having earlier quit the Liberal Party over what he considered the government's pro-British policies, campaigned against Laurier in that province. Ironically, Bourassa's attacks on Laurier in Quebec aided in the election of the Conservatives, who held more staunchly Imperialist policies than the Liberals.
...
Wikipedia


