Caliciviridae
| Caliciviridae | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group IV ((+)ssRNA) |
| Family: | Caliciviridae |
| Genera | |
Lagovirus
Nebovirus
Norovirus
Sapovirus
Vesivirus
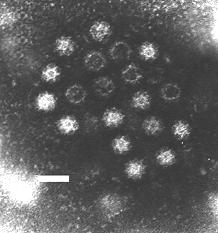
Caliciviridae is a family of viruses, members of Class IV of the Baltimore scheme. They are positive-sense, single stranded RNA which is non-segmented. There are currently seven species in this family, divided among 5 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: feline calicivirus: respiratory disease; rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus: often-fatal hemorrhages; norwalk group of viruses: gastroenteritis. Caliciviruses naturally infect vertebrates, and have been found in a number of organisms such as humans, cattle, pigs, cats, chickens, reptiles, dolphins and amphibians. The caliciviruses have a simple construction and are not enveloped. The capsid appears hexagonal/spherical and has icosahedral symmetry (T=1 or T=3) with a diameter of 35–39 nm.
Caliciviruses are not very well studied because until recently they could not be grown in culture, and there is no suitable animal model. However, the recent application of modern genomic technologies has led to an increased understanding of the virus family. A recent isolate from rhesus monkeys—Tulane virus—can be grown in culture and this system promises to increase our understanding of these viruses.
...
Wikipedia
