Calf (anatomy)
| Calf | |
|---|---|

The calf is the back portion of the lower leg
|
|
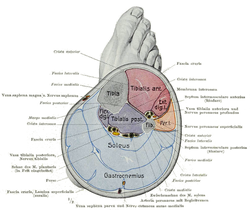
Cross-section of lower right leg, through the calf, showing its 3 compartments: anterior at upper right; lateral at center right; deep posterior at center; superficial posterior at the bottom
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sura |
| TA | A01.1.00.039 |
| FMA | 24984 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The calf (Latin: sura) is the back portion of the lower leg in human anatomy. The muscles within the calf correspond to the posterior compartment of the leg. The two largest muscles within this compartment are known together as the calf muscle and attach to the heel via the Achilles tendon. Several other, smaller muscles attach to the knee, the ankle, and via long tendons to the toes.
The calf is composed of the muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg: The gastrocnemius and soleus (composing the triceps surae muscle) and the tibialis posterior. The sural nerve provides innervation.
Medical conditions that result in calf swelling among other symptoms include deep vein thrombosiscompartment syndrome,Achilles tendon rupture, and varicose veins.
Idiopathic leg cramps are common and typically affect the calf muscles at night.Edema also is common and in many cases idiopathic. In a small study of factory workers in good health, wearing compression garments helped to reduce edema and the pain associated with edema. A small study of runners found that wearing knee-high while running significantly improved performance.
...
Wikipedia
