Achilles tendon rupture
| Achilles tendon rupture | |
|---|---|
 |
|
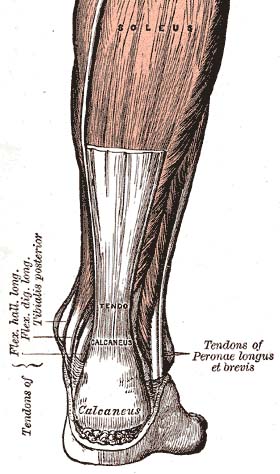
| The achilles tendon | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics |
| ICD-10 | S86.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 727.67 |
| eMedicine | sports/1 |
Achilles tendon rupture is when the achilles tendon breaks. The achilles is the most commonly injured tendon. Rupture can occur while performing actions requiring explosive acceleration, such as pushing off or jumping. The male to female ratio for Achilles tendon rupture varies between 7:1 and 4:1 across various studies.
The Achilles tendon is most commonly injured by sudden plantarflexion or dorsiflexion of the ankle, or by forced dorsiflexion of the ankle outside its normal range of motion.
Other mechanisms by which the Achilles can be torn involve sudden direct trauma to the tendon, or sudden activation of the Achilles after atrophy from prolonged periods of inactivity. Some other common tears can occur from overuse while participating in intense sports. Twisting or jerking motions can also contribute to injury.
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics, famously ciprofloxacin, are known to increase the risk of tendon rupture, particularly Achilles.
People who commonly fall victim to Achilles rupture or tear include recreational athletes, people of old age, individuals with previous Achilles tendon tears or ruptures, previous tendon injections or quinolone use, extreme changes in training intensity or activity level, and participation in a new activity.
Most cases of Achilles tendon rupture are traumatic sports injuries. The average age of patients is 29–40 years with a male-to-female ratio of nearly 20:1. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin, and glucocorticoids have been linked with an increased risk of Achilles tendon rupture. Direct steroid injections into the tendon have also been linked to rupture.
Quinolone has been associated with Achilles tendinitis and Achilles tendon ruptures for some time. Quinolones are antibacterial agents that act at the level of DNA by inhibiting DNA Gyrase. DNA Gyrase is an enzyme used to unwind double stranded DNA which is essential to DNA Replication. Quinolone is specialized in the fact that it can attack bacterial DNA and prevent them from replicating by this process, and are frequently prescribed to the elderly. Approximately 2% to 6% of all elderly people over the age of 60 who have had Achilles ruptures can be attributed to the use of quinolones.
...
Wikipedia
