Calcium nitride
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Calcium nitride
|
|
| Other names
tricalcium dinitride
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
12013-82-0 |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.435 |
| EC Number | 234-592-9 |
| PubChem | 3387080 |
| Properties | |
| Ca3N2 | |
| Molar mass | 148.25 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | red-brown crystalline solid |
| Density | 2.670 g/cm3 2.63 g/cm3 (17 °C) |
| Melting point | 1,195 °C (2,183 °F; 1,468 K) |
| decomposes | |
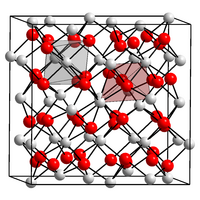
| Structure | |
| Cubic, cI80 | |
| Ia-3, No. 206 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Calcium nitride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca3N2. It exists in various forms (isomorphs), α-calcium nitride being more commonly encountered.
α-Calcium nitride adopts an anti-bixbyite structure, similar to Mn2O3, except that the positions of the ions are reversed: calcium (Ca2+) take the oxide (O2−) positions and nitride ions (N3−) the manganese (Mn3+). In this structure, Ca2+ occupies tetrahedral sites, and the nitride centres occupy two different types of octahedral sites.
Calcium nitride is formed along with the oxide, CaO, when calcium burns in air. It can be produced by direct reaction of the elements:
It reacts with water or even the moisture in air to give ammonia and calcium hydroxide:
Like sodium oxide, calcium nitride absorbs hydrogen above 350 °C:
...
Wikipedia
