Sodium oxide
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Sodium oxide
|
|||
| Other names
Disodium oxide
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
1313-59-3 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.827 | ||
| EC Number | 215-208-9 | ||
| PubChem | 73971 | ||
| UN number | 1825 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| Na2O | |||
| Molar mass | 61.98 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Density | 2.27 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 1,132 °C (2,070 °F; 1,405 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 1,950 °C (3,540 °F; 2,220 K) sublimates | ||
| sublimates at 1275 °C | |||
| reacts violently to form NaOH | |||
| Solubility | reacts with ethanol | ||
| −19.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Structure | |||
| Antifluorite (face centered cubic), cF12 | |||
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |||
| Tetrahedral (Na+); cubic (O2−) | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 72.95 J/mol·K | |||
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
73 J/mol·K | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
-416 kJ/mol | ||
|
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚)
|
-377.1 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | corrosive, reacts violently with water | ||
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 1653 | ||
| GHS pictograms |  |
||
| H314 | |||
| P280 | |||
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|||
| R-phrases | R14, R8, R34, R35 | ||
| S-phrases | (S1/2), S8, S26, S27, S36/37/39, S43, S45 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | non-flammable | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Other anions
|
Sodium sulfide Sodium selenide Sodium telluride |
||
|
Other cations
|
Lithium oxide Potassium oxide Rubidium oxide Caesium oxide |
||
|
Sodium peroxide Sodium superoxide |
|||
|
Related compounds
|
Sodium hydroxide | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Sodium oxide (SOX) is a chemical compound with the formula Na2O. It is used in ceramics and glasses, though not in a raw form. It is the base anhydride of sodium hydroxide, so when water is added to sodium oxide NaOH is produced.
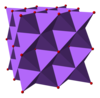
The alkali metal oxides M2O (M = Li, Na, K, Rb) crystallise in the antifluorite structure. In this motif the positions of the anions and cations are reversed relative to their positions in CaF2, with sodium ions tetrahedrally coordinated to 4 oxide ions and oxide cubically coordinated to 8 sodium ions.
Sodium oxide is produced by the reaction of sodium with sodium hydroxide, sodium peroxide, or sodium nitrite:
Most of these reactions rely on the reduction of something by sodium, whether it is hydroxide, peroxide, or nitrite.
Burning sodium in air will produce Na2O and about 20% sodium peroxide Na2O2.
Alternatively, sodium carbonate can be heated to 851 °C, producing carbon dioxide and sodium oxide.
At 208 °C, sodium ascorbate will decompose to furan derivatives and sodium oxide.
Sodium oxide is a significant component of glasses and windows although it is added in the form of "soda" (sodium carbonate). Sodium oxide does not explicitly exist in glasses, since glasses are complex cross-linked polymers. Typically, manufactured glass contains around 15% sodium oxide, 70% silica (silicon dioxide) and 9% lime (calcium oxide). The sodium carbonate "soda" serves as a flux to lower the temperature at which the silica melts. Soda glass has a much lower melting temperature than pure silica, and has slightly higher elasticity. These changes arise because the silicon dioxide and soda react to form sodium silicates of the general formula Na2[SiO2]x[SiO3].
...
Wikipedia